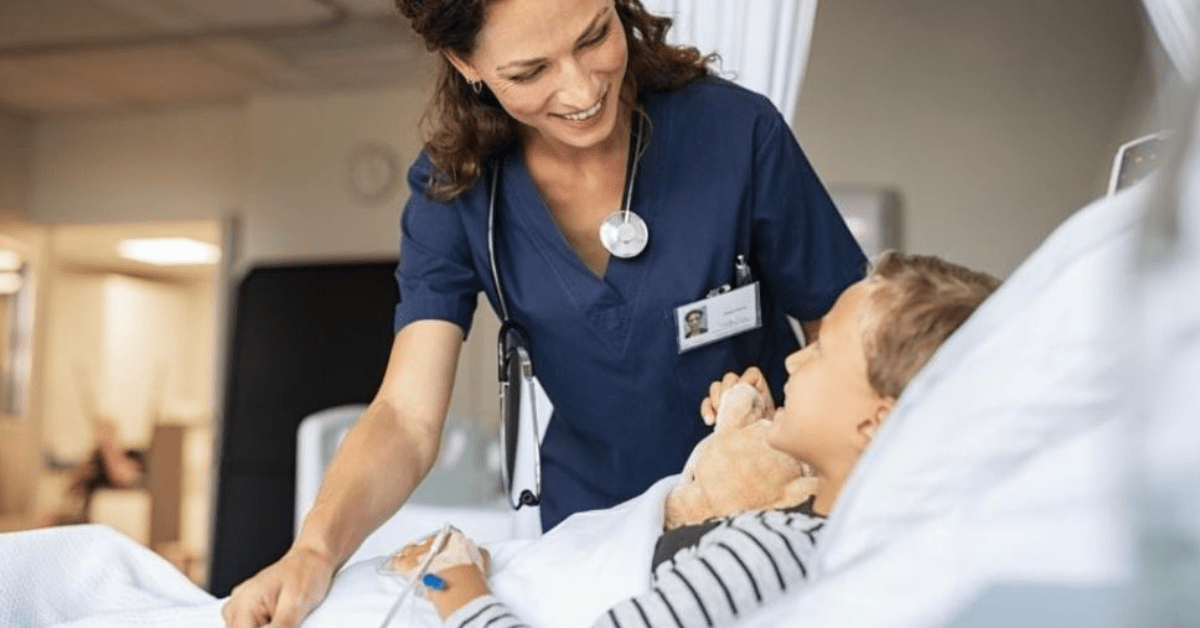
A diverse team of healthcare professionals is essential for high-quality care. By bringing together different perspectives, backgrounds and skills, healthcare providers can create more equitable, inclusive and effective healthcare strategies.
The nursing industry emphasizes the need for diversity, highlighting its significance in all areas. People from varied backgrounds and walks of life come to receive care, which illustrates the need to support various patient demographics to provide the best possible care.
An ethnically and culturally varied group of healthcare providers results in more inclusive and knowledgeable healthcare professionals who can help improve patient health outcomes.
What is diversity in healthcare?
Diversity in healthcare is about recognizing, understanding, respecting and celebrating patients’ and healthcare professionals’ different attributes, backgrounds and experiences. It also involves being conscious of one’s ethnocultural identity and understanding how that influences one’s approach to healthcare.
Diversity can also create a safe and inclusive environment where physicians, patients and caregivers feel comfortable and accepted. It can also positively affect the healthcare workforce by making it more culturally competent and improving workplace morale.
Problems with healthcare disparities
Healthcare disparities present many problems in providing quality healthcare. Some of these include:
Lack of access to healthcare
Despite efforts to reduce disparities in access to healthcare, many communities still lack access to quality healthcare services. Poor and immigrant populations are significantly affected by this problem due to their lack of financial means to pay for healthcare services or insurance coverage.
Some areas need more fundamental infrastructure, including the availability of hospitals, clinics and other healthcare providers. This lack of infrastructure can make adequate healthcare services more difficult to access, particularly in emergencies.
Reduced access to care is associated with decreased knowledge about basic health information and a lack of support from professional medical personnel, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Poor quality of care
Poor quality of care is a severe healthcare system problem, particularly for those affected by healthcare disparities. Some common disparity groups include racial and ethnic minorities, older people, people experiencing homelessness and impoverished people.
These individuals often experience worse health outcomes due to poor access to affordable healthcare resources. They may also receive a lower quality of care due to systemic biases, provider prejudice and financial barriers.
Poor quality of care can contribute to various medical conditions, including preventable illnesses, medical errors, misdiagnosis and missed health screenings.
Inadequate funds for healthcare
Inadequate funds are one of the most significant issues causing a lack of access to quality healthcare among different demographic groups. Healthcare disparities, or the differences in resources, access and quality of care experienced by various groups, are directly exacerbated by a lack of funding.
When government agencies cannot provide adequate funds to hospitals, clinics and other health-related facilities, these locations cannot offer the best possible care to their patients. This means disadvantaged individuals receive lower-quality services and lack access to the advanced treatments provided to the affluent.
In addition, an inadequate supply of funds can prevent vulnerable populations from obtaining preventative care or require them to engage in financial transactions when seeking medical assistance.
Cultural disconnects
Cultural disconnects refer to the lack of understanding and recognition of the different cultural and social contexts between healthcare personnel and patients. This can manifest in communication difficulties, misunderstanding certain cultural practices and lack of knowledge regarding culturally specific care.
Healthcare disparities occur when certain groups are excluded from or receive poorer healthcare quality than other social groups. Cultural disconnects can lead to lower quality of care for specific ethnic and racial minorities who often face language and cultural barriers.
This can lead to communication barriers and issues with interpretation, even if a common language is present among all parties. These disconnects can lead to a lack of proper diagnosis and treatment, fragmented patient care, extended hospital stays and inadequate follow-up care.
Geographical barriers
Due to physical distance, geographical barriers to healthcare refer to a need for more access to medical providers, facilities and services. This can be especially problematic in rural areas with sparse populations as well as large urban regions.
Proximity to medical services can directly impact the ability of individuals or groups to receive timely or appropriate care. Low-income, minority and otherwise disadvantaged populations may be disproportionately affected by geographical barriers to care, resulting in significant disparities in health outcomes.
Geographical barriers to healthcare can also limit the choice of providers individuals have access to and can impose higher financial costs or time commitments to travel to medical services.
Lack of insurance coverage
Insurance coverage is often linked to employment and income, meaning those lower on the socioeconomic ladder are less likely to be able to access the same quality of care. Essential medical treatments or medications can be unaffordable without insurance, leading to poorer overall health outcomes and quality of life.
A lack of coverage can deny individuals access to the latest preventative treatments and technologies, making them more likely to suffer from chronic illnesses or require emergency services.
Additionally, a lack of coverage can prevent people from seeking medical care until it’s too late. In short, lack of insurance coverage can lead to significant healthcare disparities for those who can least afford it.
Inadequate medical training
When healthcare providers, such as physicians, nurses and other medical professionals, lack adequate training, they may not recognize or understand the specific needs of underserved communities.
This lack of knowledge can lead to patients receiving less access to healthcare. A lack of proper medical training can lead providers to practice biased care or engage in inappropriate cultural practices such as derogatory language.
This lack of understanding of healthcare needs can exacerbate the disparities underserved communities face.
Strategies to combat problems with healthcare disparities
Some strategies to combat problems associated with healthcare disparities include:
Cultural competency
Cultural competency is a strategy to address healthcare disparities among different ethnic and cultural groups. This involves healthcare workers being culturally aware, understanding and accepting of cultural norms, practices, perspectives and values.
This strategy helps to foster trust and respect between healthcare providers and communities, allowing for quality and equitable healthcare delivery. It also promotes better communication between providers and patient populations, allowing for better diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Cultural competency also means understanding the context of healthcare disparities that prevent the availability of quality healthcare to specific population groups. Healthcare providers must be willing to understand, respect and promote the value of different cultures to ensure everyone has better access and outcomes.
Advocating for policy change
Advocating for policy change involves ensuring that healthcare policies are in place that promote health equity internally and externally. This includes influencing decision-makers to create and implement procedures to provide everyone with access to quality health care.
These policies may include expanding public insurance, increasing access to preventive services or providing language interpretation services for non-English speakers.
Advocates can work to ensure that local, state and national policies are created to promote health equity and that resources are in place to support these policies.
Nursing professionals who would like to enhance their advocacy skills may wish to consider enrolling in one of the many DNP programs online, available through reputable institutions such as Wilkes University. By earning a DNP, professionals are equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to provide insight into healthcare policies and deliver evidence-based practice.
This degree will give you the skills and expertise to influence healthcare outcomes through systems leadership and health policy implementation. You may also work in the following roles and impact direct patient care: nurse midwife, nurse anesthetist or nurse practitioner.
Increasing access to care
Increasing access to care includes better access to quality healthcare services such as reliable transportation, language services, comprehensive care coordination, patient education and improved access to health insurance.
By increasing access to care, underrepresented populations can receive preventative and treatment services; this can help close the care gap, reduce health disparities and improve overall health outcomes.
Additionally, providing better access to care encourages more minorities to pursue healthcare careers and improves cultural competency among healthcare providers. Enhancing access to healthcare will lead to a higher quality of care for everyone and will ultimately combat healthcare disparities.
Incentivize participation of minority patients
Incentivizing the participation of minority patients involves using financial and non-financial incentives to encourage people from minority backgrounds to access healthcare services to reduce health outcome inequalities.
These incentives include reduced fees, access to payment plans or even offering rewards such as health services or reward points. The government could incentivize the individual and the health provider for the service.
These incentives must have an excellent design to ensure their effectiveness in reducing disparities in health outcomes. Any plan should also include feedback and evaluation systems to ensure the incentive program reaches its target population.
Address social determinants of health
Addressing social determinants of health (SDH) is a strategy to combat healthcare disparities by focusing on root causes rather than symptoms.
It includes housing, nutrition, education, job opportunities, community safety, healthcare access and other essential services to support healthy, productive and successful lives.
SDH efforts must be combined with preventive and primary care interventions and health promotion activities to make healthcare more equitable. Concerted efforts are needed to address underlying social and structural determinants of health disparities and address them as an integral part of healthcare systems.
This includes managing the social and economic obstacles in underserved communities while creating greater access to quality healthcare so that healthcare disparities can be prevented or reduced.
Strengthen healthcare data collection
Strengthening healthcare data collection is crucial to improving healthcare outcomes, particularly in underserved populations. Collecting, analyzing and making data-driven decisions helps administrators better understand the challenges faced by individuals and groups of particular people.
Data also serves as a baseline for evaluating new programs and measuring healthcare systems that have been implemented to support improved health outcomes. With data as an objective tool, healthcare administrators can identify gaps, allocate resources and implement targeted interventions to address existing disparities.
Increase workforce diversity
Increasing workforce diversity includes implementing hiring practices that increase the representation of under-represented populations in the healthcare workforce. Increasing the diversity of healthcare providers and hiring staff from minority communities helps improve the quality of care and the healthcare staff’s cultural competency.
Additionally, increasing the number of minority healthcare providers in leadership positions can enhance the health outcomes of marginalized communities.
A diverse workforce can provide indispensable cultural understanding, awareness and visibility to address healthcare disparities and advocate for policies that benefit minority populations.
Create community-based programs and services
Community-based programs and services aim to address healthcare disparities by creating targeted solutions for health and social care issues. These strategies recognize the importance of an inclusive approach to tackling systemic problems.
These programs and services may include improving education access, economic resources and quality healthcare services. Creating immersive activities and outreach programs to reduce feelings of discrimination can be an effective strategy.
By designing these tailored programs, communities can address disparities in healthcare and diagnosis and give access to medical and mental health support.
Expand the role of healthcare providers
Healthcare providers can use a multi-faceted approach to reduce healthcare disparities among communities. This includes improved access to care, promoting health literacy and challenging implicit biases in healthcare delivery.
Providers can increase access to primary care services and preventative care in underserved areas. Health literacy can be improved by explaining diagnosis and treatment plans and by providing well-illustrated patient education materials.
Healthcare providers can challenge implicit biases by dealing fairly with all patients and avoiding making assumptions about a patient’s cultural background or insurance status. In addition, they can be more inclusive by having diverse healthcare teams that better represent their communities.
Final thoughts
Healthcare disparities continue to persist every day. Socioeconomic status, race, gender and other issues are at the root of these disparities. This can result in unequal access to healthcare and unequal healthcare quality, which is unacceptable in our society.
To combat the existing health disparities, we must ensure everyone has equal healthcare access and receives quality care. Achieving this can be done through measures such as increasing access to affordable care, eliminating barriers to healthcare and providing better education regarding preventive healthcare.
We must also strive to improve communication between providers and patients, advocate for evidence-based healthcare practices, and actively promote greater diversity among healthcare leaders and providers.
These strategies all work towards reducing healthcare disparities and improving healthcare quality. This will not only reduce healthcare disparities but also improve the overall health of our nation.